Structural 3D modeling has become a cornerstone in various industries due to its significant impact on design accuracy, project efficiency, and overall productivity.
Introduction to Structural 3D Modeling
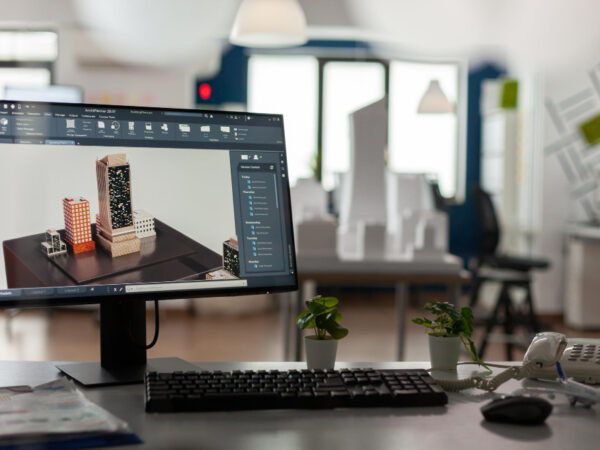
Structural 3D modeling involves creating three-dimensional representations of structures, buildings, and objects using specialized software and techniques. Unlike traditional 2D drawings, 3D models provide a more comprehensive view of the project, enabling stakeholders to visualize every aspect in detail.
Benefits of Structural 3D Modeling
Enhanced Visualization
One of the primary advantages of structural 3D modeling is its ability to enhance visualization. By creating realistic 3D renderings, designers, architects, and engineers can accurately depict how the final structure will look, helping clients and stakeholders better understand the design intent.
Improved Communication
Structural 3D models facilitate clearer communication among project teams, contractors, and clients. With a visual representation of the project, stakeholders can easily discuss design elements, identify potential issues, and make informed decisions, leading to smoother workflows and fewer misunderstandings.
Error Detection and Prevention
Another crucial benefit is the ability to detect and prevent errors early in the design phase. By simulating the construction process in a virtual environment, structural flaws, clashes, and discrepancies can be identified and addressed before actual construction begins, reducing costly rework and delays.
Cost and Time Savings
Structural 3D modeling contributes to cost and time savings by streamlining the design and construction process. With accurate measurements, material quantities, and project timelines, stakeholders can optimize resource allocation, minimize waste, and complete projects within budget and schedule.
Applications of Structural 3D Modeling
Structural 3D modeling finds extensive applications across various industries, including:
- Architecture and Construction: Architects use 3D models to create detailed building designs, while contractors rely on them for accurate construction plans and coordination.
- Engineering and Design: Engineers utilize 3D models to analyze structural integrity, perform simulations, and optimize designs for performance and safety.
- Urban Planning: City planners leverage 3D models to visualize urban developments, assess environmental impacts, and create sustainable cityscapes.
- Interior Design: Designers use 3D modeling to create immersive interior spaces, experiment with layouts, and showcase design concepts to clients.
Technologies Used in Structural 3D Modeling
Several technologies support structural 3D modeling, including:
- Building Information Modeling (BIM): BIM software allows for the creation of intelligent 3D models with detailed information about building components, materials, and performance characteristics.
- Computer-Aided Design (CAD): CAD software enables precise drafting and modeling of structural elements, providing accurate measurements and geometric representations.
- Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR): VR and AR technologies enhance the visualization of 3D models, offering immersive experiences and interactive simulations.
Challenges and Solutions in Structural 3D Modeling
Despite its benefits, structural 3D modeling presents challenges such as complexity, integration issues, and the need for skilled professionals. Solutions include:
- Embracing automation and AI to simplify modeling processes and improve accuracy.
- Integrating 3D models with other systems like project management software for seamless collaboration and data exchange.
- Investing in training programs to upskill personnel and leverage advanced modeling techniques effectively.
Future Trends in Structural 3D Modeling
The future of structural 3D modeling is shaped by emerging trends such as:
- Automation and AI Integration: AI algorithms automate repetitive tasks, generate design variations, and optimize structural performance, leading to more efficient workflows.
- Sustainability and Green Design: 3D modeling tools enable designers to explore sustainable materials, energy-efficient solutions, and environmentally friendly design practices.
- Collaboration and Cloud-Based Platforms: Cloud-based platforms facilitate real-time collaboration, data sharing, and remote access to 3D models, fostering global teamwork and project scalability.
In conclusion, structural 3D modeling plays a crucial role in modern design and construction processes, offering numerous benefits, enhancing communication, and driving innovation. As technology continues to evolve, the integration of 3D modeling with automation, sustainability practices, and collaborative platforms will shape the future of the industry.
Do you have any project requirements for structural 3D modeling, then feel free to reach out at info@shalindesigns.com or click here for more details.



